We delve into the history of the war of ideas between Weldon and Bateson, and its knock-on impact on the science of heredity all the way through the 20th century to today
All in Plants
Antony Dodd: Manipulating malaria by changing the clocks
All sorts of organisms have circadian rhythms, and Professor Antony Dodd is using our knowledge of clock genes to target malaria and herbicide use
Giles Oldroyd: Go fertilise yourself
Giles Oldroyd is finding out how plants can provide their own fertiliser with a little help from specialist microbes like fungi and bacteria.
Caroline Dean: Winter is coming
Caroline Dean has devoted her research career to understanding how plants sense and respond to the changing of the seasons.
Gunes Taylor: Genome editing in plants, animals and humans.
Gunes Taylor discusses how CRISPR/Cas9 technology may be used in agriculture, livestock and human health.
Ruth Garde: Cut+Paste - Exploring the ethical issues around genome editing
Ruth Garde is the creative producer behind Cut+Paste a hands-on exhibition at the Francis Crick Institute that aims to explore the ethical issues around gene editing and gather the public’s views about how this technology should be used.
Robin Lovell-Badge: Who should decide what is allowed when it comes to genome editing?
Robin Lovell-Badge discusses why genome editing regulations and ethical approval decisions should not be left up to scientists alone.
Kadeem Gilbert: life in a death trap
Dr Kadeem Gilbert is an ecologist and evolutionary biologist at Michegan State University who has been researching the pool of digestive juices. And it turns out that it’s not only a place where insects drown and get digested by the pitcher plant, it’s also home to a whole community of living things that are able to survive despite the harsh conditions.
Ulrike Bauer: killing on a knife edge
One group of carnivorous plants are the pitcher plants, and they’re usually found in warm, tropical habitats around the world. Dr Ulrike Bauer studies these plants at the University of Bristol to find out more about how they’re able to successfully trap insects so easily.
Tanya Renner: Creating carnivorous ketchup
We chat with Dr Tanya Renner from Pennsylvania State University who is interested not only in how these plants evolved but also whether we can add carnivorous genes into non carnivorous plants.
Hannah Rees: giving wheat jet lag
We need to make wheat a more reliable and resilient crop in the face of our ever changing climate, and that’s where geneticists like Dr Hannah Rees from the Earlham Institute in Norwich come in. Kat Arney sits down with Hannah to find out how understanding the basic biology of wheat is helping us produce a more future-proof plant.
Solar powered: the evolution of photosynthesis
Dr Kat Arney is turning the lights on, looking back at the origins of photosynthesis and the mysteries of the chloroplast genome. From The King James Bible to The Great Oxygen Catastrophe, every lungful of air you breathe has a remarkable story.
Stealing genes
Researchers have discovered that whitefly have ‘stolen’ protective genes from the plants they feed on
Here be dragons
We’re seeking the genetic and mathematical secrets of snapdragons.
Bringing Mendel to Britain
We follow William Bateson on a very special train journey in May 1900, bringing the ideas of Mendel to Britain.
The budding lady botanist - Harriet Creighton
Many people - although not enough - know about Barbara McClintock’s work on maize genetics. But how many know about her first graduate student, Harriet Creighton?
Hey, buddy
First discovered by sixteenth century doctor and botanist Johannes Thal, Arabidopsis has long been a firm favourite of geneticists who prefer their subjects to stay still in a pot.
The Onion Test
Why does an onion need five times more ‘junk DNA’ than you do?
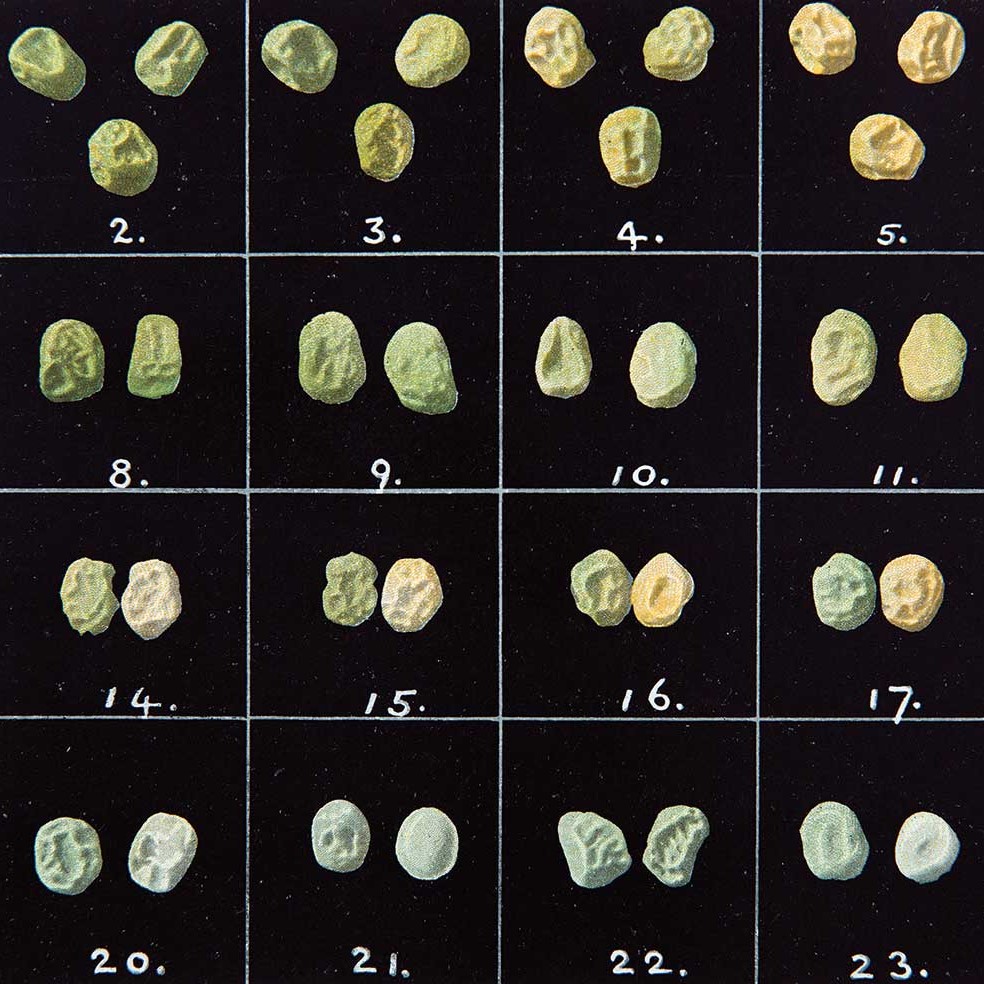
Fifty shades of peas
Gregor Mendel discovered the principles of genetics. But it turns out that people are not peas… and even peas are not peas.
What's your Flavr?
Exploring the story of the world’s first commercial GM food crop